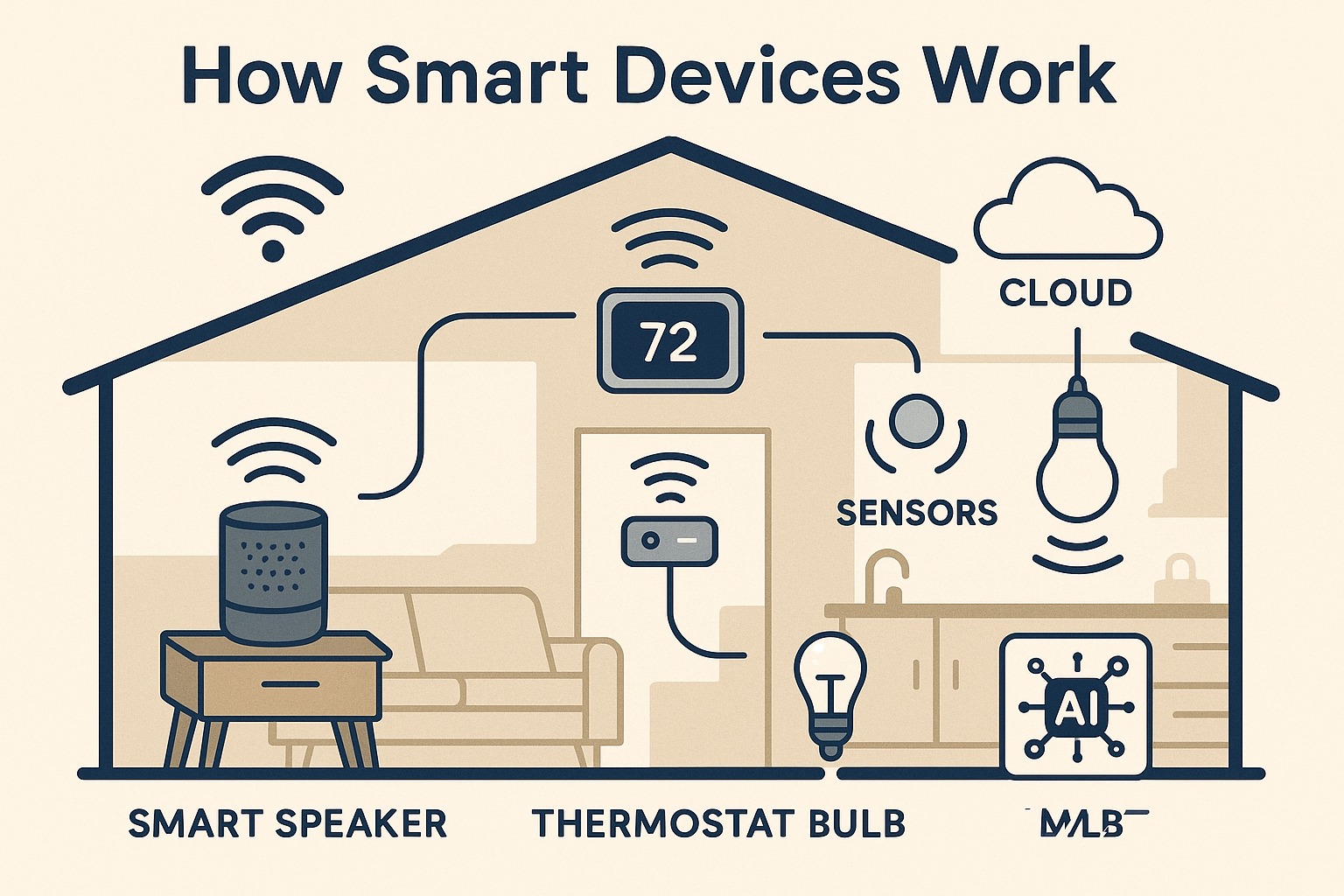
In today’s connected world, smart devices are revolutionizing how we interact with our homes and daily routines. From Wi-Fi-enabled thermostats to voice-activated lights, these intelligent gadgets use sensors, microcontrollers, and wireless protocols to function automatically and efficiently. By leveraging technologies like Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cloud connectivity, smart devices can learn your preferences, adapt to your schedule, and create a more convenient and energy-efficient living space. In this guide, we’ll break down how smart devices work, the technology behind smart homes, and what makes these devices a cornerstone of modern home automation.
Smart devices work by combining sensors, processors, and wireless communication technologies to collect data, make decisions, and automate tasks. These devices often connect to the internet or local networks, enabling remote control, voice activation, and seamless integration within a smart home ecosystem.
What Are Smart Devices?
Smart devices are everyday electronic gadgets—like thermostats, lights, plugs, or speakers—that go beyond basic functions by connecting to the internet or local networks, allowing them to interact, learn, and respond automatically. What makes a device “smart” isn’t just its function, but how it communicates, adapts, and integrates with other systems in your home.
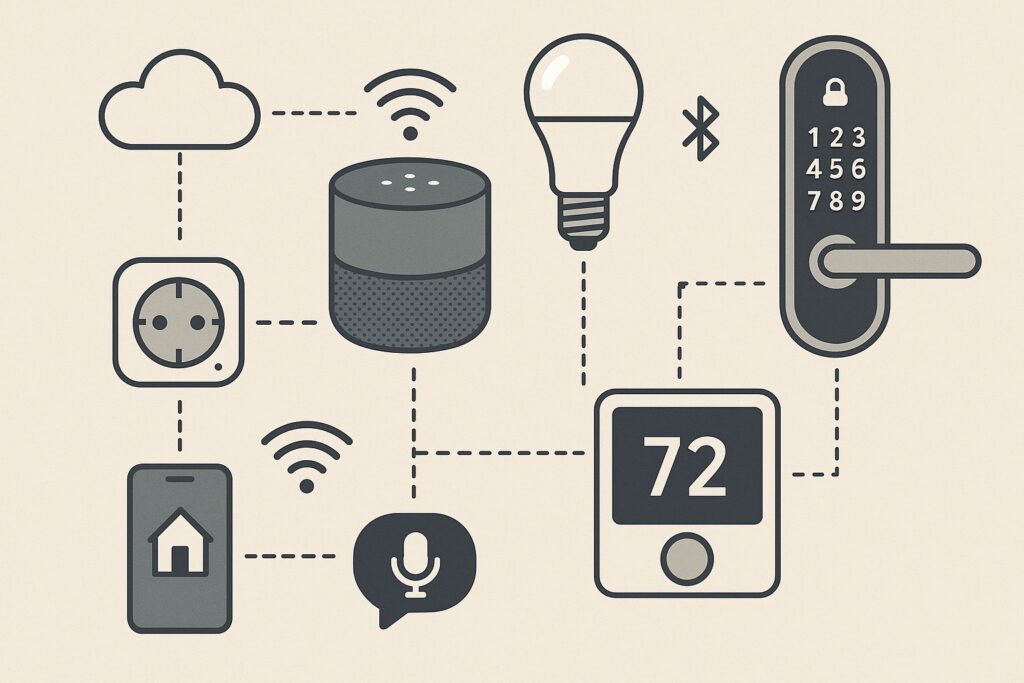
At their core, smart devices combine semantic traits like automation, connectivity, and real-time data exchange. These gadgets often use Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z-Wave to talk to other devices or your smartphone. You can control them through apps, voice assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant, or even automate them to follow routines—like turning on lights at sunset or adjusting the thermostat when you leave home.
Some of the key traits that define smart devices include:
- Remote access and control via smartphone or voice
- Data-driven responsiveness through built-in sensors
- Integration with broader smart home systems
- Self-updating software for better performance and security
You’ll often hear related terms like connected devices, intelligent electronics, or IoT (Internet of Things)—all of which refer to this new era of tech that’s designed to make life simpler, more efficient, and highly customizable.
Core Components of a Smart Device
At first glance, a smart device might seem like magic—but under the hood, it’s a mix of clever hardware and smart software working together. Whether it’s a smart thermostat, light bulb, or doorbell camera, every smart device has a few key components that make it “smart.”
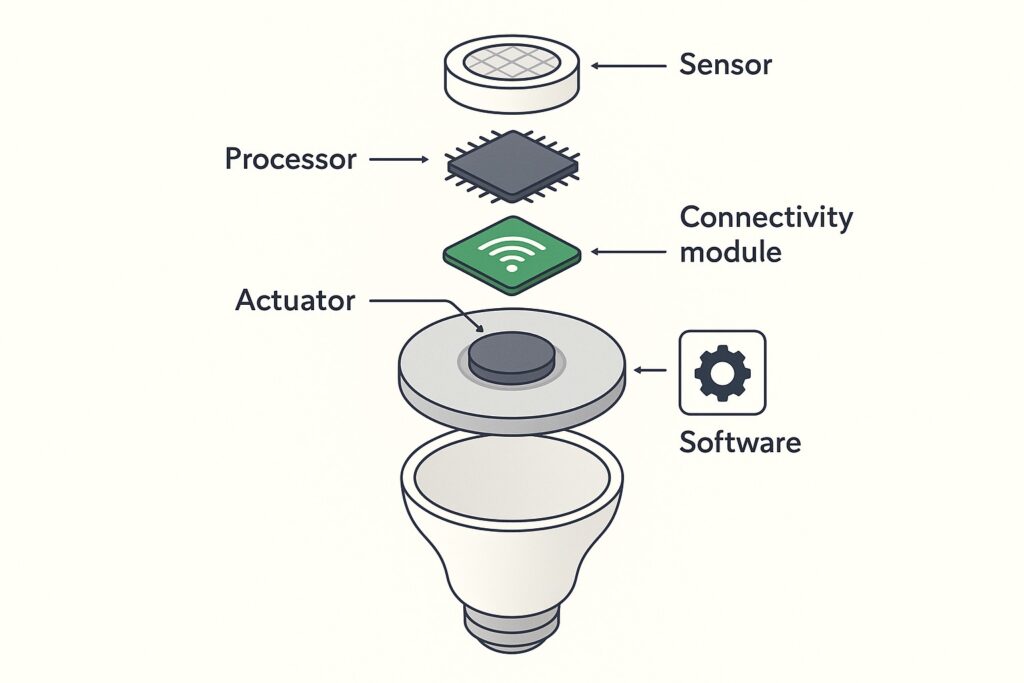
🧠 1. Sensors
Sensors are the eyes and ears of any smart device. They detect changes in the environment—like motion, temperature, humidity, or light—and send that data to the device’s processor. For example, a smart thermostat uses temperature sensors to decide when to adjust heating or cooling.
⚙️ 2. Actuators
Actuators take action based on what the sensor tells them. In a smart lock, the actuator physically moves the lock bolt when you unlock it from your phone. They’re responsible for doing the “work” the device is designed for.
💻 3. Microcontroller/Processor
This is the brain of the device. It processes the data from sensors and decides what action to take. It also manages communication between the device and your smartphone, home hub, or the cloud.
📡 4. Connectivity Module
Smart devices need a way to communicate—and that’s where the connectivity module comes in. Depending on the device, this could be Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Thread. This module handles sending and receiving data, whether it’s a command from your phone or an update from the cloud.
🔐 5. Embedded Software & Firmware
Behind the scenes, the device runs on firmware or embedded software that helps it perform its functions, stay secure, and communicate with other devices. This software is usually updated over-the-air (OTA) to fix bugs or add features.
How Smart Devices Communicate
Smart devices don’t work in isolation—they’re part of a bigger, connected ecosystem. To function smoothly, they need to communicate with each other, with your smartphone, and sometimes even with the cloud. This communication is made possible through various wireless protocols and network technologies, each with its own strengths.
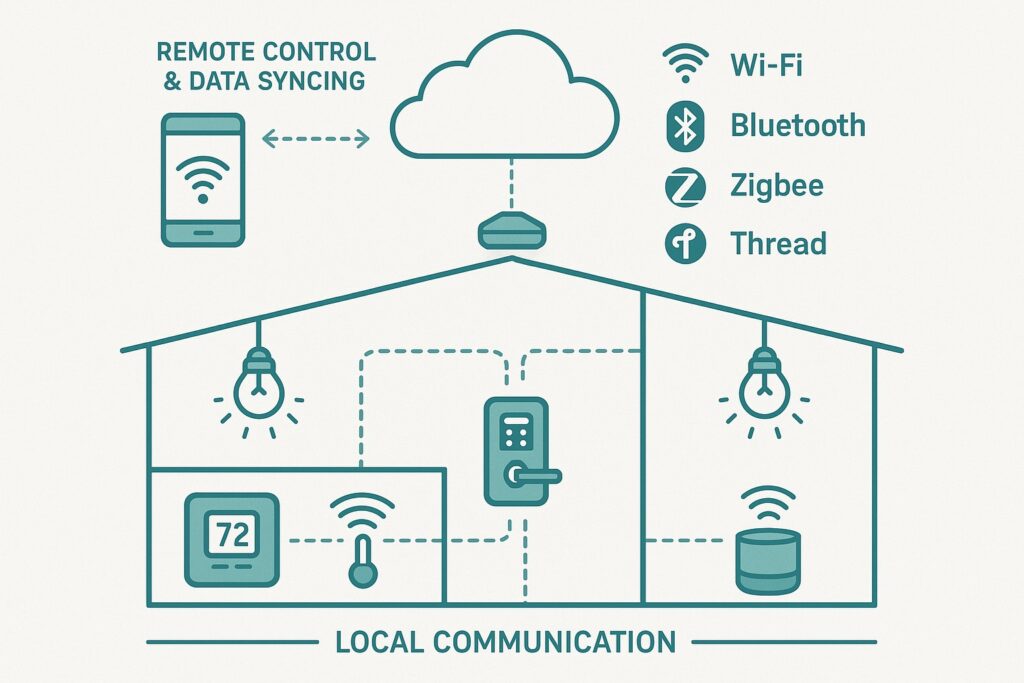
🌐 1. Wireless Protocols
Smart devices rely on different types of wireless communication protocols to send and receive data. The most common ones include:
- Wi-Fi: Offers high-speed data transfer and is perfect for devices like smart cameras or video doorbells that need constant, heavy data usage.
- Bluetooth: Great for short-range, low-energy communication—used in smart locks, fitness trackers, and some lighting systems.
- Zigbee and Z-Wave: Both are low-power mesh networks that let devices talk to each other over longer distances. They’re often used for smart lights, plugs, and sensors.
- Thread: A newer protocol designed specifically for smart home devices, offering fast, secure, and energy-efficient communication.
These protocols are the backbone of smart device interoperability, allowing gadgets from different brands to work together under one smart home platform.
☁️ 2. Cloud Connectivity
Many smart devices connect to cloud servers via the internet. This allows them to:
- Sync data
- Get software updates
- Use AI-based features like voice recognition
- Enable remote control when you’re away from home
For example, when you tell Alexa to turn off the lights, your command travels from your voice assistant → to the cloud → and then to the smart bulb.
🔄 3. Local Communication
Not all devices need the cloud to function. Some smart devices communicate locally—either directly or via a smart hub (like SmartThings or Apple HomePod). This means faster response times and better privacy since data doesn’t always have to leave your home.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Devices
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is what takes smart devices from being just “connected” to truly “intelligent.” It’s the brainpower behind features that let your smart thermostat learn your schedule, your smart speaker understand your voice commands, and your security camera detect real threats instead of just motion.
🧠 1. Machine Learning for Smarter Automation
Many smart devices use machine learning algorithms to adapt to your habits. For example, a smart thermostat like Nest doesn’t just follow a preset—it learns when you wake up, when you leave the house, and what temperature you prefer at bedtime. Over time, it creates a personalized schedule that saves energy and keeps you comfortable.
🗣️ 2. Voice Control and Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI-powered voice assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri rely on natural language processing (NLP) to understand what you’re saying, even with different accents or phrasing. This means you can say “turn off the lights in the kitchen” or “dim the kitchen lights,” and your system will get it either way. The more you use them, the smarter they get.
🔁 3. Predictive Behavior and Smart Suggestions
Smart devices can also predict your needs based on your behavior. For example, your smart lighting system might suggest dimming the lights when it notices you tend to do that around 9 PM. AI turns simple automation into context-aware intelligence, making your devices more intuitive and proactive.
Power Sources and Energy Efficiency
While smart devices are packed with high-tech features, they still need one basic thing to function: power. How a smart device is powered plays a big role in where and how it can be used, how long it lasts, and how energy-efficient it is over time.
🔋 1. Battery-Powered vs. Plug-In Devices
Many smart devices are either battery-operated or plugged into a wall outlet, depending on their use. Devices like smart door locks, motion sensors, and outdoor cameras often use batteries so they can be installed anywhere without wiring. On the flip side, devices like smart speakers, thermostats, and video doorbells are usually plug-in or hardwired to ensure consistent power.
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are common in portable smart gadgets. And some eco-friendly models even come with solar charging options, especially for outdoor use.
💡 2. Energy-Saving Features
One of the big promises of smart tech is energy efficiency—and it delivers. Many devices have built-in features designed to reduce waste and cut down your utility bills, such as:
- Sleep or standby modes that conserve power when not in use
- Motion-activated lighting that turns off automatically
- Learning thermostats that optimize heating and cooling schedules
- Smart plugs that track energy usage and allow remote shutoff
These features aren’t just convenient—they also help reduce your carbon footprint and promote sustainable smart living.
📈 3. Monitoring and Optimization
Smart plugs, energy monitors, and connected appliances often provide real-time usage stats, allowing you to track exactly how much power your devices are consuming. Some even offer tips or automation suggestions to improve efficiency over time. It’s like having an energy coach in your pocket.
How Smart Devices Connect with Each Other (Smart Home Ecosystem)
One of the most powerful aspects of smart technology is how seamlessly different devices can work together. Your smart lights, thermostat, doorbell, and speaker aren’t just individual gadgets—they’re part of a smart home ecosystem. When properly connected, they can respond to each other’s signals, run synchronized routines, and give you a truly automated living experience.
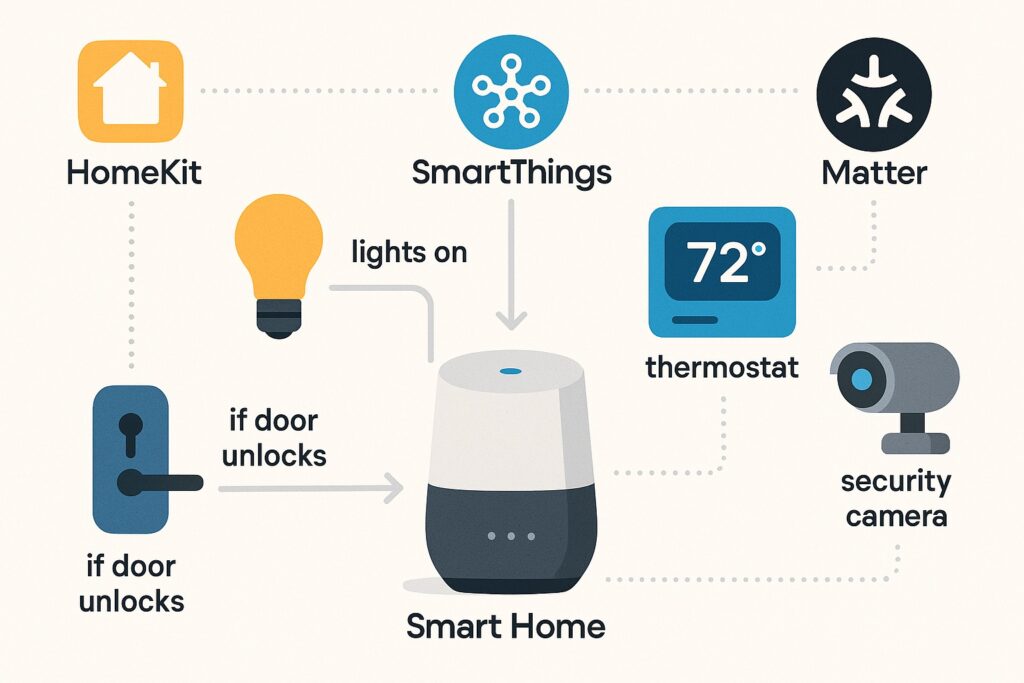
🏠 1. Integration Platforms That Make It All Work
To bring your devices into harmony, most smart homes rely on integration platforms like:
- Amazon Alexa
- Google Home
- Apple HomeKit
- Samsung SmartThings
These platforms act like a digital conductor—bringing all your IoT devices together and allowing you to control them from a single app or voice assistant.
For example, with Alexa, you could set a routine that turns off your lights, locks the doors, and lowers the thermostat—all with one voice command or tap.
🔄 2. Automation Through Triggers and Routines
What makes a smart home feel truly smart is automation. Devices can be set to react to each other through “If This, Then That” logic:
- If the front door unlocks, turn on the hallway lights.
- If it’s sunset, close the smart blinds and turn on indoor lighting.
- If no motion is detected after 10 minutes, turn off the AC.
These actions are often controlled through smart hubs or cloud-based platforms that manage the device interactions based on your preferences.
🔗 3. Unified Control and Interoperability
With the rise of new standards like Matter, connecting devices from different brands is becoming easier. No more worrying about whether your smart bulb will work with your smart switch. Interoperability is improving, and that means more flexibility for you to build your ideal smart home setup without getting locked into a single brand.
Security and Privacy in Smart Devices
As smart devices become more deeply integrated into our lives, it’s natural to wonder: Is my personal data safe? While these gadgets offer incredible convenience, they also open the door to potential security risks and privacy concerns. The good news is—when used wisely, smart home devices can be both secure and private. It just takes a little awareness and a few best practices.
🔐 1. The Risks: What Could Go Wrong?
Smart devices are always listening, learning, and transmitting data—whether it’s a smart speaker hearing your voice commands or a camera streaming footage to the cloud. If not properly protected, these devices can be:
- Hacked by outsiders
- Tracked for behavioral data
- Exposed through outdated firmware
Cybercriminals often target weak spots like default passwords, unencrypted connections, or vulnerable Wi-Fi networks.
🛡️ 2. Built-in Security Features to Look For
Luckily, many reputable brands now prioritize IoT security. Look for devices that include:
- End-to-end encryption to protect your data in transit
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) for logging into apps
- Automatic firmware updates to patch known vulnerabilities
- Local data storage (instead of cloud-only) for added privacy
Some smart home hubs even allow you to create private, local-only networks so your data doesn’t leave your home at all.
🧠 3. How to Protect Your Smart Home
Being proactive makes a big difference. Here are some privacy best practices:
- Always change the default password immediately
- Use a separate Wi-Fi network for smart devices
- Keep firmware and apps up to date
- Turn off features like always-on microphones if not needed
- Review your device’s data-sharing settings and permissions
At the end of the day, security in smart devices is a shared responsibility—manufacturers are building smarter defenses, and users must take smart steps to stay protected.
Real-Life Examples of Smart Devices at Work
Sometimes the best way to understand how smart devices work is to see them in action. These real-life examples show how smart technology makes everyday living more convenient, energy-efficient, and secure—all without you lifting a finger.
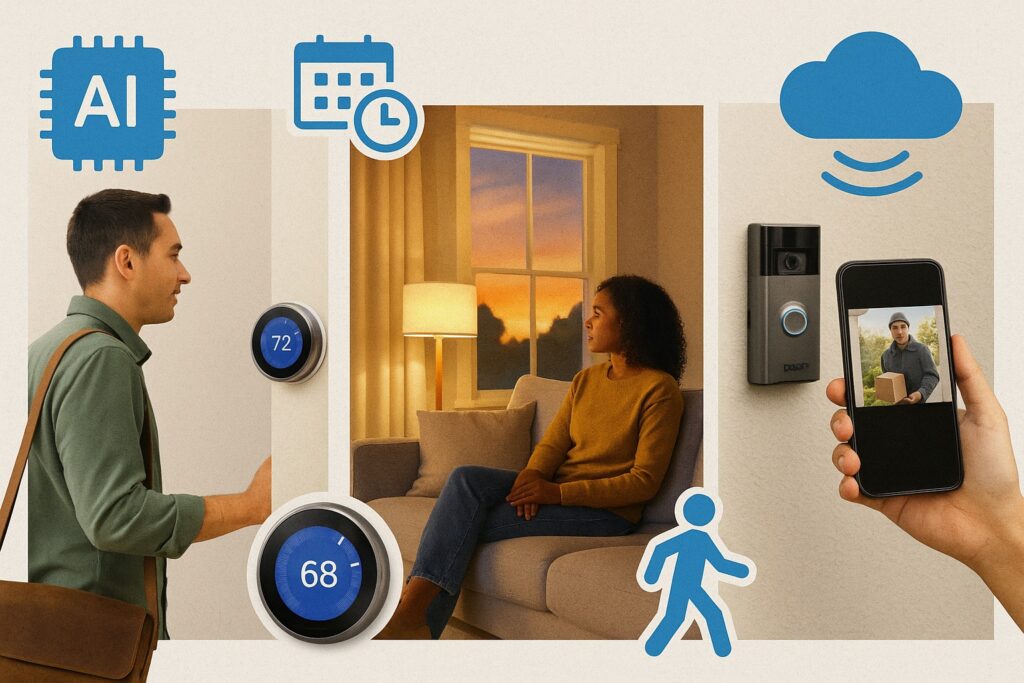

🏠 1. Smart Thermostat That Learns Your Routine
Let’s say you leave for work around 8 AM and return by 6 PM. A smart thermostat like Nest or Ecobee tracks your patterns over time. It automatically lowers the temperature after you leave and warms your home before you return—saving energy while keeping you comfortable. That’s AI-powered home automation in real life.
💡 2. Smart Lights That Follow the Sun
Imagine your lights turning on gradually as the sun sets, without any manual input. Smart lighting systems like Philips Hue or LIFX can be synced to your local sunset times or motion sensors. They even adjust brightness depending on time of day—bringing a cozy, customized ambiance to your space. This is a great example of context-aware smart lighting in action.
🔒 3. Smart Locks and Video Doorbells That Boost Security
Ever left the house and wondered if you locked the door? With a smart lock like August or Yale, you can check and control it from your phone. Add in a Ring or Google Nest video doorbell, and you can see who’s at your door, speak to visitors, or get alerts when motion is detected. This combo delivers real-time smart home security and peace of mind—whether you’re at home or away.
Pros and Cons of Using Smart Devices
Smart devices have come a long way, turning once-basic home appliances into intelligent tools that respond to your needs. But like any technology, they come with both perks and limitations. Let’s break down the real-world advantages and disadvantages of using smart home devices, so you can decide if they’re right for you.
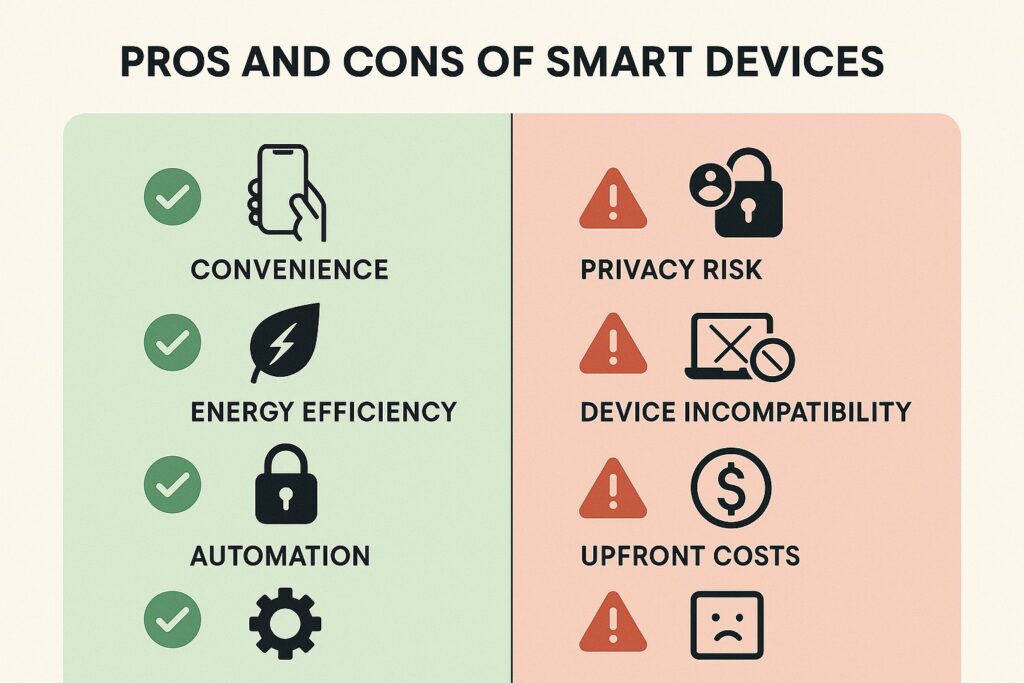
✅ Pros of Smart Devices
1. Convenience at Your Fingertips
Smart devices are all about hands-free control and remote access. Whether you’re adjusting the thermostat from your bed or turning off lights with your voice, the convenience is unmatched.
2. Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Many smart devices—like thermostats, plugs, and lighting—are built to optimize energy usage. By learning your habits or responding to occupancy, they help lower utility bills and promote eco-friendly home automation.
3. Improved Security and Peace of Mind
Smart security systems, video doorbells, and smart locks offer real-time alerts, remote monitoring, and added layers of control. You can keep an eye on your home no matter where you are.
4. Customization and Automation
Create personalized routines like “good morning” or “bedtime” to trigger multiple devices at once. This level of smart home customization makes daily routines effortless and tailored to your lifestyle.
❌ Cons of Smart Devices
1. Privacy Concerns
Since smart devices collect and transmit data, privacy risks can arise—especially if devices lack proper encryption or have outdated firmware.
2. Compatibility Issues
Not all smart gadgets work together out of the box. Without a central hub or platform compatibility, setting up a cohesive system can feel frustrating.
3. High Initial Costs
While you may save money in the long run, some smart devices require a higher upfront investment compared to traditional appliances.
4. Tech Reliance and Glitches
Smart homes depend on Wi-Fi stability and app functionality. If your internet goes down—or an app update causes bugs—you may lose access to essential functions.
The Future of Smart Devices
Smart devices have already transformed our homes, but the journey is just getting started. As technology continues to evolve, the future of smart devices is set to be more connected, more intuitive, and more sustainable than ever before.
🚀 1. Smarter Integration with the Matter Protocol
One of the most exciting advancements is the adoption of Matter, a universal connectivity standard developed by major tech companies like Apple, Google, Amazon, and Samsung. With Matter, devices from different brands will work together effortlessly—finally solving the headache of smart home compatibility.
No more guessing which devices work with which apps. In the near future, your lights, locks, cameras, and appliances will speak a common smart language, making setup and automation easier for everyone.
🧠 2. AI-Driven Personalization and Predictive Automation
Smart devices are becoming more context-aware, using artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict what you need before you ask. Imagine your thermostat adjusting the temperature because it knows it’s about to rain—or your lights dimming because your calendar says you’re starting a Zoom call.
This kind of proactive automation is where smart homes become truly intelligent, responding not just to commands, but to behavior, location, and environmental cues.
🌱 3. Energy Harvesting and Sustainable Design
The future is also greener. Emerging devices will use energy harvesting—pulling power from sunlight, vibrations, or heat. That means more battery-free sensors, less waste, and lower environmental impact. Combined with better energy usage tracking, smart homes are on track to support eco-friendly living at scale.
🌍 4. Ambient Computing and Seamless Experiences
We’re moving toward a world where smart technology fades into the background. With ambient computing, devices will blend into your home—always available, but never in the way. Think smart mirrors, invisible sensors, or lights that follow your movement without a command.
FAQs
Most smart devices use Wi-Fi to connect to your home network. Once connected, they can send and receive data, access cloud services, and be controlled remotely through an app or voice assistant. Some low-power gadgets use Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z-Wave, especially when paired with a smart home hub.
Yes—some smart devices can work locally through Bluetooth, Zigbee, or Z-Wave, especially when connected to a smart hub. These devices don’t need constant internet but may lose features like remote control or cloud-based automation when offline.
Smart speakers and assistants are designed to activate only after hearing a “wake word” like “Hey Google” or “Alexa.” While they do listen for that keyword, they’re not recording all the time. However, it’s important to review privacy settings and manage data permissions in your device’s app.
Not always. Different brands may use different communication standards or platforms. However, with the rise of Matter, a new interoperability protocol, many smart devices will soon work together more easily across systems like Google Home, Alexa, and Apple HomeKit.
Most smart devices are designed to be energy-efficient, especially those that run on batteries or low-voltage power. In fact, many help reduce overall energy consumption by optimizing usage—like turning off lights when no one’s in the room or lowering the thermostat when you’re away.
🧾 Conclusion: Smarter Living Starts Here
Smart devices have moved far beyond novelty—they’re now essential tools for creating a home that’s safer, more efficient, and perfectly tailored to your daily routine. Whether it’s the convenience of voice commands, the energy savings of smart thermostats, or the peace of mind from real-time security alerts, the smart home ecosystem brings real value to modern living.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even deeper integration, better interoperability, and more personalized automation—all making your home work for you, not the other way around.
👉 Ready to Start Building Your Smart Home?
If you’re just starting out, check out our Beginner’s Guide to Smart Home Technology — it’s packed with tips to help you choose the right devices, understand setup basics, and avoid common pitfalls.
Want to go deeper into specific areas? You might also enjoy:
- Smart Home Hubs: Which One Is Best for You?
- How to Set Up Smart Lights Like a Pro
- Wi-Fi vs Zigbee vs Z-Wave: What’s the Difference?
✅ Smart Home Starter Checklist
Everything You Need to Begin Your Smart Home Journey. You can click here to download the Smart Home Starter Checklist PDF.